Special Effects
- What is Draw?
- Parts of the main Draw window
- Choosing and defining colors
- Positioning objects with Snap functions
- Positioning objects with guiding lines
- The basic drawing shapes
- Drawing geometric shapes
- Selecting objects
- Moving and dynamically adjusting an object’s size
- Editing objects
- Using styles
- Special effects
- Combining multiple objects
- Aids for positioning objects
- Inserting and editing pictures
- Working with 3D objects
- Exporting graphics
- Adding comments to a drawing
Special Effects
With Draw, you can apply many special effects to objects and groups of objects. This section describes a few of these effects. The icons for these effects are available on the Drawing toolbar under the ![]() icon. More effects include distorting, shadows, and transparency can be found in Chapter 4 (Changing Object Attributes) in the Draw Guide.
icon. More effects include distorting, shadows, and transparency can be found in Chapter 4 (Changing Object Attributes) in the Draw Guide.
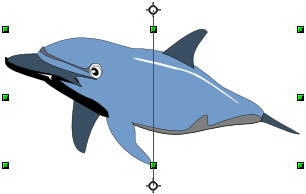
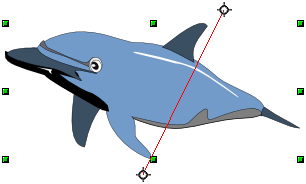
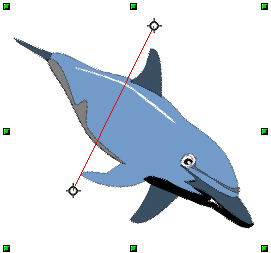
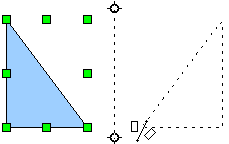
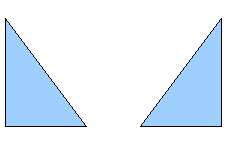
Flip an Object
Mirror Copies
Move the axis of symmetry to the desired location of the mirror axis. Copy the object to the clipboard. Flip the object, then click on an empty area of the Draw screen in order to deselect the object. Paste from the clipboard to put a copy of the object in its original location, and now you have a mirror copy.
 |
 |
Distorting an Image
There are three tools through the Effects icon that let you drag the corners and edges of an object to distort the image.
The Distort tool distorts an object in perspective, the Set to Circle (slant) and Set in Circle (perspective) tools both create a pseudo three-dimensional effect. See Chapter 4 in the Draw Guide for details.
Dynamic Gradients
You can control transparency gradients in the same manner as color gradients. Both types of gradient can be used together. With a transparency gradient, the direction and degree of an object's fill color changes from opaque to transparent (in a regular gradient, the fill changes from one color to another, but the degree of transparency remains the same). See Chapter 4 in the Draw Guide for details.
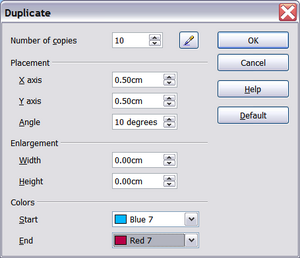
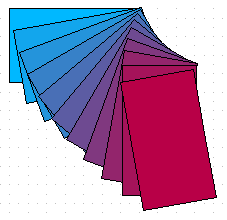
Duplication
Duplication makes copies of an object while applying a set of changes (such as color or rotation) to the duplicates. The result of a duplication is a new group of objects.
To start duplication, click on an object or group and choose Edit → Duplicate. The dialog shown in Figure 156 appears. When the options selected in that dialog are applied to a blue rectangle, they produce the result shown in Figure 157.
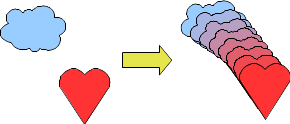
Cross-fading
Cross-fading transforms a shape from one form to another. The result is a new group of objects including the start and end points and the intermediate steps.
To carry out a cross-fade, first select two objects (hold the ⇧ Shift key while selecting each object in turn) and then choose Edit → Cross-fading.
On the Cross-fading dialog, choose the number of increments (transition steps). You probably want to have Cross-fade attributes and Same orientation both checked. The end result is shown in Figure 159.
| Content on this page is licensed under the Creative Common Attribution 3.0 license (CC-BY). |