Formatting pages
- The Writer interface
- Working with documents
- Working with text
- Formatting text
- Formatting pages
- Adding comments and graphics to a document
- Creating a table of contents, index, or bibliography
- Printing from Writer
- Sending a fax
- Tracking changes to a document
- Fields, mail merge, master documents, forms
- Linking to another part of a document
Writer provides several ways for you to control page layouts:
- Page styles
- Columns
- Frames
- Tables
- Sections
For more information, see Chapter 4 (Formatting Pages) in the Writer Guide.
Which layout method to choose?
The best layout method varies depending on what the final document should look like and what sort of information will be in the document. Here are some examples.
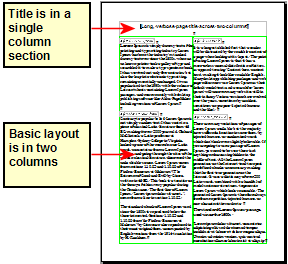
For a book similar to this user guide, with one column of text, some figures without text beside them, and some other figures with descriptive text, use page styles for basic layout, and tables to place figures beside descriptive text when necessary.
For an index or other document with two columns of text, where the text continues from the left-hand column to the right-hand column and then to the next page, all in sequence (also known as “snaking columns” of text), use page styles (with two columns). If the title of the document (on the first page) is full-page width, put it in a single-column section.
For a newsletter with complex layout, two or three columns on the page, and some articles that continue from one page to some place several pages later, use page styles for basic layout. Place articles in linked frames and anchor graphics to fixed positions on the page if necessary.
For a document with terms and translations to appear side-by-side in what appear to be columns, use a table to keep items lined up, and so you can type in both “columns”.
A header is an area that appears at the top of a page. A footer appears at the bottom of the page. Information, such as page numbers inserted into a header or footer, displays on every page of the document with that page style.
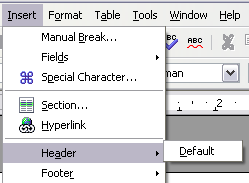
To insert a header, click Insert > Header > Default (or the page style, if not Default) as shown below.
Other information such as document titles and chapter titles is often put into the header or footer. These items are best added as fields. That way, if something changes, the headers and footers are updated automatically. Here is one common example.
To insert the document title into the header:
- Click File > Properties > Description and type a title for your document.
- Add a header (Insert > Header > Default).
- Place the cursor in the header part of the page.
- Select Insert > Fields > Title. The title should appear on a gray background (which does not show when printed and can be turned off).
- To change the title for the whole document, go back to File > Properties > Description.
Fields are covered in detail in Chapter 14 (Working with Fields) in the Writer Guide.
For more about headers and footers, see Chapter 4 (Formatting Pages) and Chapter 6 (Introduction to Styles) in the Writer Guide.
Numbering pages
To automatically number pages:
- Insert a header or footer, as described in Creating headers and footers.
- Place the cursor in the header or footer where you want the page number to appear and click Insert > Fields > Page Number.
Including the total number of pages
To include the total number of pages (as in “page 1 of 12”):
- Type the word “page” and a space, then insert the page number as above.
- Press the spacebar once, type the word “of” and a space, then click Insert > Fields > Page Count.
Restarting page numbering
Often you will want to restart the page numbering at 1, for example on the page following a title page or a table of contents. In addition, many documents have the “front matter” (such as the table of contents) numbered with Roman numerals and the main body of the document numbered in Arabic numerals, starting with 1.
You can restart page numbering in two ways.
Method 1:
- Place the cursor in the first paragraph of the new page.
- Click Format > Paragraph.
- On the Text Flow tab of the Paragraph dialog (Figure 18 on page 18), select Breaks.
- Select Insert and then With Page Style and specify the page style to use.
- Specify the page number to start from, and then click OK.
Method 2:
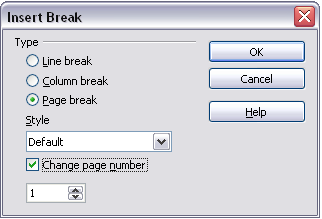
- Insert > Manual break.
- By default, Page break is selected on the Insert Break dialog.
- Choose the required page Style.
- Select Change page number.
- Specify the page number to start from, and then click OK.
Changing page margins
You can change page margins in two ways:
- Using the page rulers—quick and easy, but does not have fine control.
- Using the Page Style dialog—can specify margins to two decimal places.
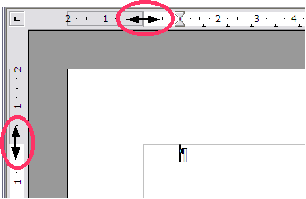
To change margins using the rulers:
- The gray sections of the rulers are the margins. Put the mouse cursor over the line between the gray and white sections. The pointer turns into a double-headed arrow.
- Hold down the left mouse button and drag the mouse to move the margin.
To change margins using the Page Style dialog:
- Right-click anywhere on the page and select Page from the pop-up menu.
- On the Page tab of the dialog, type the required distances in the Margins boxes.
| Content on this page is licensed under the Creative Common Attribution 3.0 license (CC-BY). |