AutoCorrecting
- Selecting text
- Cutting, copying, and pasting text
- Finding and replacing text and formatting
- Inserting special characters
- Formatting paragraphs
- Formatting characters
- Autoformatting
- Creating numbered or bulleted lists
- Using footnotes and endnotes
- Checking spelling
- Using language tools
- Using the thesaurus
- Hyphenating words
- Using word completion
- Using AutoText
- Line numbering
- Undoing and redoing changes
- Tracking changes to a document
- Inserting notes
- Linking to another part of a document
- Working with hyperlinks
- Tips and tricks
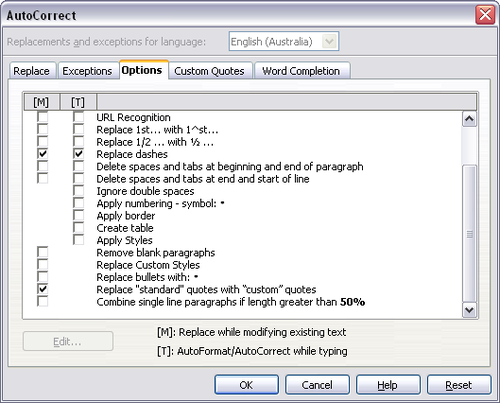
Writer can be set to automatically format parts of a document according to the choices made on the Options page of the AutoCorrect dialog box (Tools > AutoCorrect > Options).
The Help describes each of these choices and how to activate the autoformats. Some common unwanted or unexpected formatting changes include:
- Horizontal lines. If you type three or more hyphens (---), underscores (___) or equal signs (===) on a line and then press Enter the paragraph is replaced by a horizontal line as wide as the page minus any indentation of the preceding paragraph of which the line is the lower border.
- Bulleted and numbered lists. A bulleted list is created when you type a hyphen (-), asterisk (*), or plus sign (+), followed by a space or tab at the beginning of a paragraph. A numbered list is created when you type a number followed by a period (.), followed by a space or tab at the beginning of a paragraph. Automatic numbering is only applied to paragraphs formatted with the Default, Text body or Text body indent paragraph styles.
| If you notice unexpected formatting changes occurring in your document, this is the first place to look for the cause. |
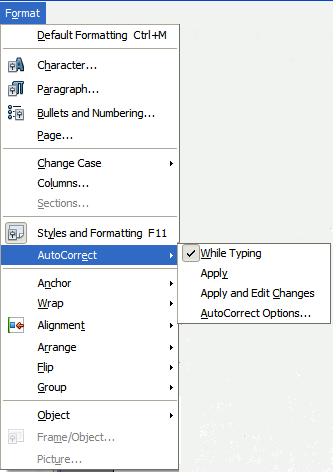
To turn autoformatting on or off, go to Format > AutoCorrect and select or deselect the items on the submenu.
- While Typing automatically formats the document while you type.
- If While Typing is deselected, you can select Apply to automatically format the file.
- Apply and Edit Changes automatically formats the file and then opens a dialog box where you can accept or reject the changes.
- AutoCorrect Options opens the AutoCorrect dialog box where you can set conditions for replacements and exceptions for the language you are using.
Defining Strings in AutoCorrect
Writer's AutoCorrect function has a long list of common misspellings and typing errors, which it corrects automatically. For example, "hte" will be changed to "the". Select Tools > AutoCorrect to open the AutoCorrect dialog. There you can define which strings of text are corrected and how. In most cases, the defaults are fine.
- To stop Writer from replacing a specific spelling, use Tools > AutoCorrect Options > Replace, highlight the word pair and click Delete.
- To add a new spelling to correct, type it into the Replace and With boxes and click New.
- See the different pages of the dialog box for the wide variety of other options available to fine-tune AutoCorrect.
| AutoCorrect can be used as a quick way to insert special characters. For example, (c) will be autocorrected to ©. You can add your own special characters. |
Writer's AutoCorrect function has a long list of common misspellings and typing errors, which it corrects automatically. For example, "hte" will be changed to "the". Select Tools > AutoCorrect to open the AutoCorrect dialog. There you can define which strings of text are corrected and how. In most cases, the defaults are fine.
- To stop Writer from replacing a specific spelling, use Tools > AutoCorrect Options > Replace, highlight the word pair and click Delete.
- To add a new spelling to correct, type it into the Replace and With boxes and click New.
- See the different pages of the dialog box for the wide variety of other options available to fine-tune AutoCorrect.
| AutoCorrect can be used as a quick way to insert special characters. For example, (c) will be autocorrected to ©. You can add your own special characters. |
| Content on this page is licensed under the Creative Common Attribution 3.0 license (CC-BY). |