Difference between revisions of "Documentation/How Tos/Calc: SUMX2PY2 function"
From Apache OpenOffice Wiki
< Documentation | How Tos
m |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{DISPLAYTITLE:SUMX2PY2 function}} |
| − | + | {{Documentation/CalcFunc ArraysTOC | |
| − | + | |ShowPrevNext=block | |
| − | + | |PrevPage=Documentation/How_Tos/Calc:_SUMX2MY2_function | |
| − | + | |NextPage=Documentation/How_Tos/Calc:_SUMXMY2_function | |
| − | | | + | }}__NOTOC__ |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |PrevPage= Documentation/How_Tos/Calc:_SUMX2MY2_function | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | }} | + | |
| − | + | ||
== SUMX2PY2 == | == SUMX2PY2 == | ||
| Line 40: | Line 15: | ||
:<i>Advanced topic:</i> | :<i>Advanced topic:</i> | ||
| − | :<tt>'''SUMX2PY2'''</tt> evaluates its parameters <tt>'''x'''</tt> and <tt>'''y'''</tt> as [[Documentation/How_Tos/Using Arrays|array formulas]] but does not need to be entered as an array formula. In other words it can be entered with the | + | :<tt>'''SUMX2PY2'''</tt> evaluates its parameters <tt>'''x'''</tt> and <tt>'''y'''</tt> as [[Documentation/How_Tos/Using Arrays|array formulas]] but does not need to be entered as an array formula. In other words, it can be entered with the {{key|Enter}} key, rather than {{key|Cntrl|Shift|Enter}}. See the example below. |
=== Example: === | === Example: === | ||
Latest revision as of 10:51, 30 January 2024
SUMX2PY2
Returns the sum of the squares of all elements of two matrices.
Syntax:
SUMX2PY2(x; y)
- x and y are arrays or ranges of the same size. SUMX2PY2 calculates
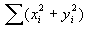 for the i elements in the arrays or ranges.
for the i elements in the arrays or ranges.
- Advanced topic:
- SUMX2PY2 evaluates its parameters x and y as array formulas but does not need to be entered as an array formula. In other words, it can be entered with the ↵ Enter key, rather than Cntrl + ⇧ Shift + ↵ Enter . See the example below.
Example:
SUMX2PY2(A1:A2; {2|1})
- where cells A1 and A2 contain 4 and 3 respectively, returns (42+22) + (32+12) = 30.
Advanced topic (parameter evaluated as array formula):
SUMX2PY2(A1:A2+1; {2|1})
- when entered 'normally' (not as an array formula), and where cells A1 and A2 contain 3 and 2 respectively, returns ((3+1)2+22) + ((2+1)2+12) = 30. SUMX2PY2 forces (A1:A2+1) to be evaluated as an array formula (internally returning the array {4|3}).
See Also