Difference between revisions of "Documentation/How Tos/Calc: SUMPRODUCT function"
From Apache OpenOffice Wiki
< Documentation | How Tos
(→See also:: added fns) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== SUMPRODUCT == | == SUMPRODUCT == | ||
| − | + | Returns the sum of the products of corresponding array elements. | |
=== Syntax: === | === Syntax: === | ||
| − | <tt>'''SUMPRODUCT( | + | <tt>'''SUMPRODUCT(array1; array2; ... array30)'''</tt> |
| − | : <tt>''' | + | : <tt>'''array1'''</tt> to <tt>'''array30'''</tt> are up to 30 arrays or ranges whose corresponding elements are to be multiplied. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
:<tt>'''SUMPRODUCT'''</tt> evaluates in array mode, but does not need to be entered as an [[Documentation/How_Tos/Using Arrays|array formula]]. | :<tt>'''SUMPRODUCT'''</tt> evaluates in array mode, but does not need to be entered as an [[Documentation/How_Tos/Using Arrays|array formula]]. | ||
| − | : <tt>'''SUMPRODUCT'''</tt> can also be used to sum cells where a specified condition is true - see '''[[Documentation/How_Tos/Conditional Counting and Summation|Conditional Counting and Summation]]'''. | + | : You can use <tt>'''SUMPRODUCT'''</tt> to calculate the scalar product of two vectors. |
| + | |||
| + | : <tt>'''SUMPRODUCT'''</tt> can also be used to sum cells where a specified condition is true - see '''[[Documentation/How_Tos/Conditional Counting and Summation|Conditional Counting and Summation]]''' and the example below. | ||
=== Example: === | === Example: === | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
<br style="clear:both;" /> | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
| − | <tt>'''<nowiki> | + | <tt>'''<nowiki>SUMPRODUCT(A1:A6=”red”; B1:B6=”big”; C1:C6)</nowiki>'''</tt> |
:returns the sum of cells in <tt>'''C1:C6'''</tt> whose corresponding entries in the A column are <tt>'''red'''</tt> and in the B column are <tt>'''big'''</tt>. | :returns the sum of cells in <tt>'''C1:C6'''</tt> whose corresponding entries in the A column are <tt>'''red'''</tt> and in the B column are <tt>'''big'''</tt>. | ||
Revision as of 07:06, 15 March 2008
SUMPRODUCT
Returns the sum of the products of corresponding array elements.
Syntax:
SUMPRODUCT(array1; array2; ... array30)
- array1 to array30 are up to 30 arrays or ranges whose corresponding elements are to be multiplied.
- SUMPRODUCT evaluates in array mode, but does not need to be entered as an array formula.
- You can use SUMPRODUCT to calculate the scalar product of two vectors.
- SUMPRODUCT can also be used to sum cells where a specified condition is true - see Conditional Counting and Summation and the example below.
Example:
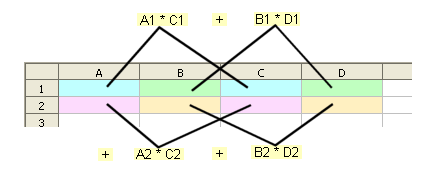
SUMPRODUCT(A1:B2; C1:D2)
- returns A1*C1 + B1*D1 + A2*C2 + B2*D2:
SUMPRODUCT(A1:A6=”red”; B1:B6=”big”; C1:C6)
- returns the sum of cells in C1:C6 whose corresponding entries in the A column are red and in the B column are big.
See also:
SUM, SUMIF, SUMSQ, SUMX2MY2, SUMX2PY2, SUMXMY2