Modifying images
When you insert a new image, you may need to modify it to suit the document. This section describes the use of the Picture toolbar, resizing, cropping, and a workaround for rotating a picture. Changes made in Calc do not affect the original picture, whether it is embedded or linked.
Calc provides many tools for working with images. These tools are sufficient for most people's everyday requirements. However for professional results it is generally better to use an image manipulation program such as GIMP to modify images (for example, to crop, resize, rotate, and change color values) and then insert the result into Calc. GIMP is an open-source graphics program that can be downloaded from http://www.gimp.org/downloads/.
Using the picture toolbar
When you insert an image or select one already present in the document, the Picture toolbar appears. You can set it to always be present (View > Toolbars > Picture). Picture control buttons from the Picture toolbar can also be added to the Standard Toolbar. See Setting Up and Customizing Calc for more information.
This toolbar can be either floating or docked. Figure 4 shows what the Picture toolbar looks like when it is floating. A brief explanation of the function of the tools is given in Table 1. A more detailed exploration is provided in the Draw Guide.
Two other toolbars can be opened from this one: the Graphic Filter toolbar, which can be torn off and placed elsewhere on the window, and the Color toolbar, which opens as a separate floating toolbar.
From these toolbars, you can apply small corrections to the graphic or obtain special effects.
Table 1: Picture toolbar functions (from left to right)
| Icon | Name | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| From File | Use of this icon is described in Inserting an image from a file. | |
| Filter | Displays the Graphic Filter toolbar. | |
| Graphics Mode | The drop-down list reveals several color modes. | |
| Color | Opens the Color toolbar. | |
| Transparency | Sets the transparency of the selected image. | |
| Line | Adjusts the border style of the selected image. | |
| Area | Fills an area with the selected color or pattern. | |
| Shadow | Adds a drop shadow to the edges of the picture. | |
| Crop | Opens the Crop dialog, where you can remove a selected part of the picture. | |
| Anchor | Toggles between anchoring the image to the cell or to the page. | |
| Bring to Front | Brings the selected image to the front of the stack. | |
| Send to Back | Pushes the selected image to the rear of the stack. | |
| To Foreground / Background | Allows image to float in the foreground or makes it part of the background (behind the cells). | |
| Alignment | If two or more pictures are selected, adjusts the horizontal and vertical alignment of the pictures in relation to each other. |
Choosing a graphics mode
You can change color images to grayscale by selecting the image and then selecting Grayscale from the Graphics mode list.
Table 2: Graphics modes
| Graphics mode | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Default | Keeps the picture the same as it was inserted. |
| Grayscale | Shows the picture in gradual shades of gray. |
| Black / White | Converts the picture into a monochromatic black and white image. |
| Watermark | Makes the picture into a watermark that blends into the background. |
Using graphic filters
Click the Filter icon to display the Graphic Filter toolbar, which provides options for applying basic photographic and effect filters to images from within Calc. To "tear off" this toolbar and place it anywhere on the screen, click on the three parallel lines and drag it away.
The graphic filters available in Calc
Table 3: Graphic filters and their effects
Adjusting colors
Use the Color toolbar to adjust an image’s red, green, and blue channels independently, as well as its brightness, contrast and gamma.
Setting transparency
Modify the percentage value in the Transparency box ![]() on the Picture toolbar to make the image more transparent. This is particularly useful when creating a watermark or when wrapping the image in the background.
on the Picture toolbar to make the image more transparent. This is particularly useful when creating a watermark or when wrapping the image in the background.
Customizing lines, areas, and shadows
The Line, Area, and Shadow icons opens dialogs where you can customize them. Details are in the Draw Guide.
Cropping pictures
When you are only interested in a section of the image for the purpose of your document, you may wish to crop (cut off) parts of it. The user interface in Calc for cropping an image is not very friendly. so it may be a better choice to use a graphics package.
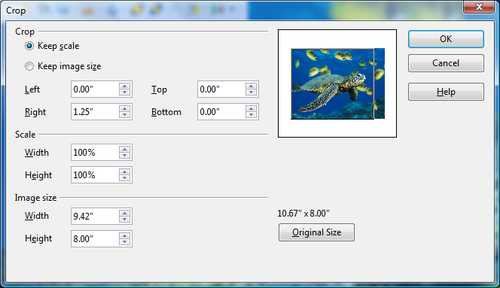
Click the Crop icon to open a dialog where you can select which portion of the image you want to remove.
It is not possible to use the mouse to select the area to be cropped, as you can in Draw. Instead, in the Crop dialog, specify how far from the top, bottom, left and right borders the crop should be, as illustrated below. On the thumbnail in the figure, notice that the cropped selection is highlighted with an inner rectangle.
On the Crop dialog, you can control the following parameters:
Keep scale / Keep image size
When Keep scale is selected (default), cropping the image does not change the scale of the picture.
When Keep image size is selected, cropping enlarges (for positive cropping values), shrinks (for negative cropping values), or distorts the image so that the image size remains constant.
Left, Right, Top, and Bottom
The image is cropped by the amount entered in these boxes. For example, a value of 3cm in the Left box cuts 3 cm from the left side of the picture.
- When Keep scale is selected, the size of the image also changes, so in this example the width will be reduced by 3 cm.
- When Keep image size is selected, the remaining part of the image is enlarged (when you enter positive values for cropping) or shrunk (when you enter negative values for cropping) so that the width and height of the image is not changed.
Width and Height
The Width and Height fields under either Scale or Image size change as you enter values in the Left, Right, Top, and Bottom fields. Use the thumbnail next to these fields to determine the correct amount by which to crop.
The cropped shape is always a rectangle; more complex cropped shapes are not possible in Calc. Instead, use a dedicated photo or image editing software for the job, then import the image into Calc.
Resizing an image
To resize an image.
- Click the picture, if necessary, to show the green resizing handles.
- Position the pointer over one of the green resizing handles. The pointer changes shape giving a graphical representation of the direction of the resizing.
- Click and drag to resize the picture.
- Release the mouse button when satisfied with the new size.
The corner handles resize both the width and the height of the graphic object simultaneously, while the other four handles only resize one dimension at a time.
Resizing a bit-mapped (raster) image such as a photograph adversely affects the resolution, causing some degree of blurring. It is better to use a graphics package to size your picture correctly before inserting it into your document, if possible.
For more accurate resizing, use the Position and Size dialog.
Rotating a picture
Calc does not provide a tool for rotating a picture, but you can use this workaround:
- Open a new Draw or Impress document.
- Insert the image you want to rotate.
- Select the image, then in the Drawing toolbar (shown by default at the bottom of the window in Impress and Draw), select the Rotate icon
 .
. - Rotate the image as desired. Use the red handles at the corners of the picture and move the mouse in the direction you wish to rotate. By default the picture rotates around its center (indicated by a black crosshair), but you can change the pivot point by moving the black crosshair to the desired rotation center.
- Select the rotated picture by pressing Ctrl+A, then copy the image to the clipboard with Ctrl+C.
- Finish by going back to the Calc document, place the cursor where the image is to be inserted, and press Ctrl+V.
| Content on this page is licensed under the Creative Common Attribution 3.0 license (CC-BY). |