Difference between revisions of "User:Regina"
(→No Symbolic π) |
|||
| Line 213: | Line 213: | ||
=== No Symbolic π === | === No Symbolic π === | ||
| − | + | From mathematics you know <tt>sin(π)= 0</tt> and you know that <tt>tan(π/2)</tt> is undefined. But you cannot get this in Calc, because the value π is always treated as rounded floating point number. It makes no difference using <tt>PI()</tt> or <tt>RADIANDS(180)</tt>. Calc cannot evaluate π symbolically as computer algebra systems do. That is no special limitation of Calc, but other often used spreadsheet applications work only numerically too. | |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 17:33, 6 October 2008
- native language
- German
- active in project
- de, qa. sc
- OOo user name
- regina
- special interest
- www.ooowiki.de
Sandbox
CHISQDIST
Calculates values for a χ2-distribution.
Syntax
CHISQDIST(x; k; Cumulative)
- x is the number, at which you will evaluate the χ2-distribution.
- k sets the degrees of freedom for the χ2-distribution
- Constraint: k must be a positive integer
- Cumulative is a logical value.
- In the case Cumulative=TRUE() the cumulative distribution function is used, in the case Cumulative=FALSE() the probability density function. This parameter is optional. It is set to TRUE() if missing.
Semantic
CHISQDIST(x;k;FALSE()) returns values of the probability density function for the χ2-distribution:
CHISQDIST(x;k;TRUE()) returns the left tail probability for the χ2-distribution:
Example
CHSQDIST(2.7;3;FALSE())
- returns approximately 0.1699395239
CHSQDIST(2.7;3;TRUE())
- returns approximately 0.5597727056
Remarks
If you need CHISQDIST(x;k;TRUE()) with a non integer parameter k, then use GAMMADIST(x;k/2;2) instead.
In the density case the internal calculation uses logarithmic- and exponential function, if x >1425 or x · k > 1391000. Therefore it is less accurate then than in other cases.
See also:
CHISQINV, LEGACY.CHIDIST, LEGACY.CHIINV, CHITEST
Functions listed alphabetically, Functions listed by category
Issues:
This function is expected for OOo3.1
CHISQINV
Calculates the inverse of the CHISQDIST function.
Syntax
CHISQINV(p; k)
- k is the degrees of freedom for the χ2-distribution.
- Constraint: k must be a positive integer
- p is the given probability
- Constraint: 0 ≤ p < 1
Semantic
- CHISQINV(p; k) returns the value x, such that CHISQDIST(x; k;TRUE()) = p.
Example
CHISQINV(0.5; 9)
- returns approximately 8.342832692
.
Remarks
If you need CHISQINV(p;k) for a non interger parameter k, then use GAMMAINV(p;k/2;2) instead.
See also:
Functions listed alphabetically, Functions listed by category
Issues:
- This function is expected for OOo3.1
GAMMA
Returns the values of the Gamma function.
Syntax
GAMMA(x)
- x is a number.
- Constraint: If x is an integer, then x must be positive.
Semantic
GAMMA(x) calculates
-
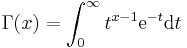 .
.
Example
- GAMMA(4) = 6.0 exact
- GAMMA(34.56) ≈ 6.2336323276E+037
- GAMMA(−4) not defined
Remarks
For x < 0.5 Eulers reflection formula is used.
The Gamma function has poles for negative integers and for zero. Near the poles the values are less accurate.
If x is a positive integer, then
But be aware, that OpenOffice.org has only a precision of 15 digits, therefore the results for x > 21 are rounded.
See also:
GAMMALN, GAMMADIST, GAMMAINV, FACT
Functions listed alphabetically, Functions listed by category
Issues:
This function is expected for OOo3.1.
Accuracy
Precision in Calc
Calc uses for its calculation floating point numbers in double precision as defined in IEEE 754 standard. You get the best representation in a spreadsheet cell using the scientific format with format code 0.00000000000000E+000. But because a binary format is used internally, the numbers in calculation might differ slightly from the shown decimal values. Only integers in the range  can be represented exactly in the internal format.
can be represented exactly in the internal format.
Although you can force Calc to show 15 decimal digits, these might not be all accurate. This article lists some of the problems.
Cancellation
If you subtract two non integer numbers, which have nearly the same value, the result has less significant digits then the initial values.
| A | B | C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9.99411764795882E-001 | =0.999411764795882 | |
| 2 | 9.99411764705882E-001 | =1699/1700 | |
| 3 | 8.99997854020285E-011 | =A1-A2 | |
| 4 | 8.99996470588235E-011 |
Cell A4 shows the correct result of  , calculated with a computer algebra system with high precision.
, calculated with a computer algebra system with high precision.
Converting Inaccuracy
Most non integer numbers have infinite decimal places in binary format, which has to be rounded somewhere. Calculating with this rounded values and converting back to decimal format gives different values then calculating manually in decimal format.
| A | B | C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.99999876543210000000 | =0.99999876543210000000 | |
| 2 | 0.00000123456790002141 | =1-A1 | |
| 3 | |||
| 4 |
No Symbolic π
From mathematics you know sin(π)= 0 and you know that tan(π/2) is undefined. But you cannot get this in Calc, because the value π is always treated as rounded floating point number. It makes no difference using PI() or RADIANDS(180). Calc cannot evaluate π symbolically as computer algebra systems do. That is no special limitation of Calc, but other often used spreadsheet applications work only numerically too.
| A | B | C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.63317787283838E+016 | =TAN(PI()/2) | |
| 2 | 1.22460635382238E-016 | =SIN(RADIANS(180)) | |
| 3 |


