Difference between revisions of "NL/Documentation/How Tos/Calc: functie LIJNSCH"
From Apache OpenOffice Wiki
< NL | Documentation | How Tos
(→Syntaxis:) |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
: <tt>'''GegevensX'''</tt> is een corresponderend bereik van één enkele rij of kolom die de <i>X</i>-coördinaten specificeert. Als <tt>'''GegevensX'''</tt> wordt weggelaten wordt als standaard <tt>'''1, 2, 3, ..., n'''</tt> ingevuld. Als er meer dan één verzameling variabelen is, mag <tt>'''GegevensX'''</tt> een bereik zijn met overeenkomende meerdere rijen of kolommen. | : <tt>'''GegevensX'''</tt> is een corresponderend bereik van één enkele rij of kolom die de <i>X</i>-coördinaten specificeert. Als <tt>'''GegevensX'''</tt> wordt weggelaten wordt als standaard <tt>'''1, 2, 3, ..., n'''</tt> ingevuld. Als er meer dan één verzameling variabelen is, mag <tt>'''GegevensX'''</tt> een bereik zijn met overeenkomende meerdere rijen of kolommen. | ||
| − | : <tt>'''LIJNSCH'''</tt> | + | : <tt>'''LIJNSCH'''</tt> vindt een rechte lijn ''y'' = ''a'' + ''bx'' die het beste bij de gegevens past, met behulp van lineaire regressie (de "least squares"-methode). Met meer dan één verzameling van variabelen is de rechte lijn in de vorm ''y'' = ''a'' + ''b<sub>1</sub>x<sub>1</sub>'' + ''b<sub>2</sub>x<sub>2</sub>'' ... + ''b<sub>n</sub>x<sub>n</sub>''. |
| − | : | + | : als <tt>'''Lineairtype'''</tt> is <tt>'''ONWAAR'''</tt> wordt de gevonden rechte lijn gedwongen om door de oorsprong te gaan (de constante ''a'' is nul; ''y'' = ''bx''). Indien weggelaten is <tt>'''Lineairtype'''</tt> standaard <tt>'''WAAR'''</tt> (de lijn wordt niet gedwongen door de oorsprong te gaan). |
| − | : <tt>'''LIJNSCH '''</tt> | + | : <tt>'''LIJNSCH '''</tt> geeft een tabel (matrix) terig van statistieken zoals hieronder en moet worden ingevoerd als een [[Documentation/nl/How_Tos/Matrices gebruiken|matrixformule]] (bijvoorbeeld door '''Ctrl-Shift-Enter''' te gebruiken in plaats van alleen '''Enter''') |
| − | : | + | : als <tt>'''Statistieken'''</tt> wordt weggelaten of <tt>'''ONWAAR'''</tt> is, wordt alleen de bovenste regel van de statistiekentabel teruggegeven. Indien <tt>'''WAAR'''</tt> wordt de gehele tabel teruggegeven. |
[[Image:Calc_linest_output.png|right]] | [[Image:Calc_linest_output.png|right]] | ||
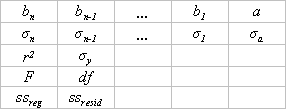
| − | : ''b<sub>1</sub>'' | + | : ''b<sub>1</sub>'' tot en met ''b<sub>n</sub>'' zijn de lijnverlopen; ''a'' is het snijpunt met de ''Y''-as. |
| − | : ''σ<sub>1</sub>'' | + | : ''σ<sub>1</sub>'' tot en met ''σ<sub>n</sub>'' zijn de standaard foutwaarden voor de lijnverlopen; ''σ<sub>a</sub>'' is de standaard foutwaarde voor het snijpunt met de ''Y''-as. |
| − | :''r<sup>2</sup>'' is | + | :''r<sup>2</sup>'' is de determinatie-coëfficient ([[Documentation/nl/How_Tos/Calc: functie R.KWADRAAT|R.KWADRAAT]]); ''σ<sub>y</sub>'' is de standaard foutwaarde voor de schatting van ''Y''. |
| − | : ''F'' is | + | : ''F'' is de F-statistiek (F-waargenomen waarde); ''df'' is het aantal vrijheidsgraden. |
| − | : ''ss<sub>reg</sub>'' is | + | : ''ss<sub>reg</sub>'' is de regressie-som van vierkanten; ''ss<sub>resid</sub>'' is de residuale som van vierkanten. |
<br style="clear:both;" /> | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
Revision as of 15:14, 30 December 2008
LIJNSCH
Geeft een tabel met statistieken terug voor een rechte lijn die het beste past voor een gegevensverzameling.
Syntaxis:
LIJNSCH(GegevensY; GegevensX; Lineairtype; Statistieken)
- GegevensY is een bereik van één enkele rij of kolom die de Y-coördinaten specificeert in een verzameling gegevenspunten.
- GegevensX is een corresponderend bereik van één enkele rij of kolom die de X-coördinaten specificeert. Als GegevensX wordt weggelaten wordt als standaard 1, 2, 3, ..., n ingevuld. Als er meer dan één verzameling variabelen is, mag GegevensX een bereik zijn met overeenkomende meerdere rijen of kolommen.
- LIJNSCH vindt een rechte lijn y = a + bx die het beste bij de gegevens past, met behulp van lineaire regressie (de "least squares"-methode). Met meer dan één verzameling van variabelen is de rechte lijn in de vorm y = a + b1x1 + b2x2 ... + bnxn.
- als Lineairtype is ONWAAR wordt de gevonden rechte lijn gedwongen om door de oorsprong te gaan (de constante a is nul; y = bx). Indien weggelaten is Lineairtype standaard WAAR (de lijn wordt niet gedwongen door de oorsprong te gaan).
- LIJNSCH geeft een tabel (matrix) terig van statistieken zoals hieronder en moet worden ingevoerd als een matrixformule (bijvoorbeeld door Ctrl-Shift-Enter te gebruiken in plaats van alleen Enter)
- als Statistieken wordt weggelaten of ONWAAR is, wordt alleen de bovenste regel van de statistiekentabel teruggegeven. Indien WAAR wordt de gehele tabel teruggegeven.
- b1 tot en met bn zijn de lijnverlopen; a is het snijpunt met de Y-as.
- σ1 tot en met σn zijn de standaard foutwaarden voor de lijnverlopen; σa is de standaard foutwaarde voor het snijpunt met de Y-as.
- r2 is de determinatie-coëfficient (R.KWADRAAT); σy is de standaard foutwaarde voor de schatting van Y.
- F is de F-statistiek (F-waargenomen waarde); df is het aantal vrijheidsgraden.
- ssreg is de regressie-som van vierkanten; ssresid is de residuale som van vierkanten.
Example:
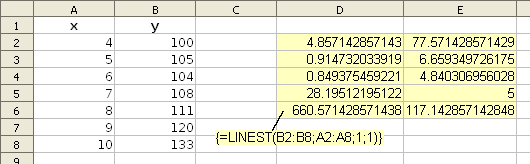
- In the example above, cells A2:B8 contain the x,y values for a set of points. LIJNSCH(B2:B8;A2:A8;1;1) returns the statistics for the best fit line through those points.
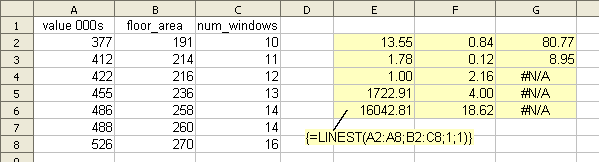
- In the example above, you measure the floor area and count the windows of a sample of houses in the area, and make a table with the corresponding sale value (cells A2:C8). To predict the value of other houses in the area you might use: value = a + b1*floor_area + b2*num_windows, where a, b1 and b2 are constants. LIJNSCH(A2:A8;B2:C8;1;1) returns appropriate statistics for that equation.
See also:
LOGSCH, TREND, R.KWADRAAT, SNIJPUNT, STIJGING
Hoe matrices te gebruiken in Calc
Functions listed alphabetically, Functions listed by category
Problemen:
- U moet goed op de hoogte zijn van de betrokken statistiek.
- Lege cellen in de uitvoer-matrix tonen #N/B (in Calc en Excel).