Working with Text
Template:Documentation/DraftPage
In Writer, you can use the toolbars, the sidebar and menus (normal and contextual) to modify text. For example, modify the selected paragraph through Format → Paragraph (choose Character to format text). Alternatively, right click the selection and choose Paragraph or Character.
Formatting tools are available through the Format menu or a right click on the page. But it is important to note that these options only modify the corresponding page style. In Writer there is no direct formatting for pages, page formatting can only be done through styles. For this reason, we will leave the details on how to format pages to the corresponding section for page styles.
Contents
Selecting Text
In Writer, in order to work with text, you need to select it.
Selecting a piece of text, or consecutive pieces of text, is relatively simple.
Using the cursor, left click the text, and drag until the desired text is selected. You can also use selection shortcuts by left clicking the text. Single words can be selected with a double left click, a sentence selected with a triple left click, and a paragraph selected with a quadruple left click.
With the keyboard, use the navigation arrows to choose the text, hold down the ⇧ Shift key and select text area with the arrow keys.
To quickly select content on the entire page, press Control + A , or go to Edit → Select All.
Selecting items that are not consecutive
- Using the cursor, select the first piece of text.
- Hold down the Control key (continue holding until all selections are complete), and use the cursor to select the next piece of text.
- Repeat until all selections are made.
Selecting a vertical block of text
Text may be separated by spaces or tabs in a vertical block. To select text in this form, change the selection mode to block by choosing Edit → Selection Mode → Block Area or left click on STD in the status bar until it changes to BLK.
Now you can make your selection as you would with consecutive text selection.
Cutting, copying and pasting text
Text can be moved within a document, or between documents by cutting or copying and subsequently pasting the text.
Cutting text entails removing it entirely and relocating it within the document. Copying text creates a duplicate to be placed within the document.
To cut or copy (with text selected) you can use:
- Keyboard shortcuts: Control + X (cut) or Control + C (copy)
- Menu selections: Edit → Cut or Edit → Copy
- Contextual menus: Right click text selection and choose Cut or Copy
- Icon sources:
 Cut or
Cut or  copy
copy
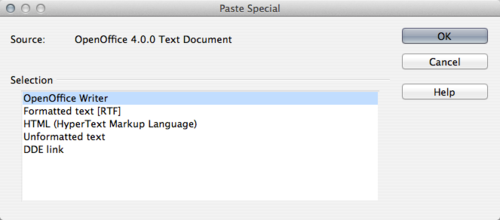
Pasting text places the cut or copied text in the document. When pasting text, the formatting result depends on the source and how you paste it.
To paste and retain original formatting use:
- Keyboard shortcut: Control + V
- Menu selection: Edit → Paste
- Contextual menu: Right click and choose Paste
- Icon source:
 Paste
Paste
To paste and take on formatting of the surrounding text:
- Choose the arrow to the right of the paste icon, and choose Unformatted text
- Select Edit → Paste Special → Unformatted text
For other paste formatting options, choose from the drop down menu of the paste icon or the Paste Special dialog box.
Numbered and bulleted lists
There are several ways to create numbered or bulleted lists:
- Auto-formatting (covered later in this chapter)
- List Styles (covered in the chapter on Styles)
- The Numbering
 and Bullets
and Bullets  icons on the paragraph formatting toolbar. The use of these icons will be described in the section below.
icons on the paragraph formatting toolbar. The use of these icons will be described in the section below.
To produce a numbered or bulleted list, select the paragraphs in the list and choose the appropriate icon.
Using the Bullets and Numbering Toolbar
With a numbered or bulleted list active, a contextual toolbar will open.
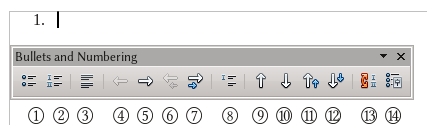
The buttons, numbered on the screenshot, perform the following actions:
- Bullets ON/OFF
- Numbering ON/OFF
- Numbering OFF
- Promote one level
- Demote one level
- Promote one level with sub-points
- Demote one level with sub-points
- Insert an unnumbered entry
- Move line up
- Move line down
- Move line up with sub-points
- Move line down with sub-points
- Restart numbering
- Bullets and Numbering dialog box
The options in the Bullets and Numbering dialog box are the same as when editing a list style, so these properties will be covered in the chapter on List Styles.
Nested Lists
As mentioned earlier, list sub-points refer to the levels of a numbered list or bullet, see example below:
- First
- Sub First
- Second
- Sub Second
- Sub Sub Second
- Sub Second
To change the level of one line in the list, either use the Promote/Demote Level ![]() icons in the Bullets and Numbering toolbar, or place the cursor at the beginning of the line and press Tab ⇆ or ⇧ Shift + Tab ⇆ .
icons in the Bullets and Numbering toolbar, or place the cursor at the beginning of the line and press Tab ⇆ or ⇧ Shift + Tab ⇆ .
Autotext
Use AutoText to insert text, tables, fields and other items for reuse, by assigning a key combination to the item for retrieval.
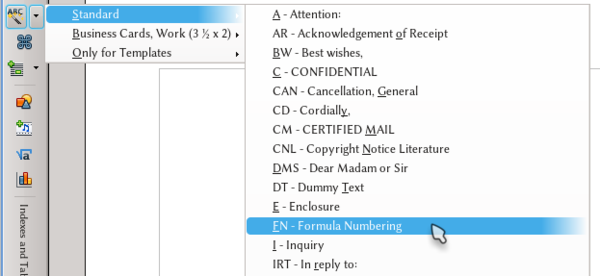
For example, by typing dt and F3 , a long paragraph with a sample text will insert into the document (note: "dt" stands for "dummy text" and different acronyms may apply to non-English versions: use Edit → AutoText to see the one appropriate for your language). Typing fn and F3 will produce a table with one row and two columns, with a Math object on the left cell and a variable on the other.
Both examples show what AutoText does and its use, to introduce a document snip previously defined in any place, using only an abbreviation and a keyboard shortcut.
Inserting an AutoText
Insert an AutoText by typing the abbreviation followed by F3 .
To view the available abbreviations, you can choose Edit → AutoText ( Ctrl + F3 ), but there is an easier method: Activating the Insert toolbar. By choosing the AutoText icon, you can view the AutoText categories and their respective abbreviations.
Defining an AutoText
- Select the content you want to use for an AutoText. The content can be anything: text, tables, pictures, frames, sections, etc.
- With the content selected, go to Edit → AutoText.
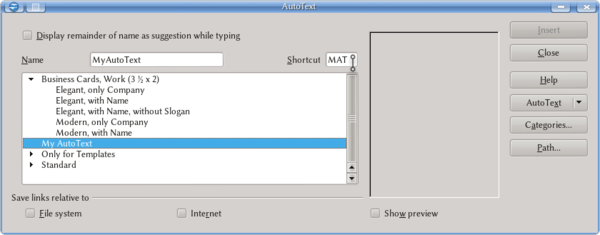
- The AutoText dialog box will appear. Provide a name for your entry in the Name box. Writer will suggest a shortcut, which you can change.
- In the box to the left, choose a category for the entry, where the AutoText will be classified.
- Select the AutoText button to the right, and select either New (text only) (for the AutoText to take on formatting where it is inserted into the document) or New (for the AutoText to retain its formatting).
- Select Close to return to the document.
| If the AutoText contains a table, it is necessary to select at least one line before and one line after the table, otherwise only the content and not the table itself will go into the AutoText. |
Inside the AutoText dialog box, note the following features:
- With the option Display remainder of the name as suggestion while typing enabled, Writer will suggest an AutoText if you start to type the AutoText name. The suggestion will appear in a pop-up box, and pressing ↵ Enter will insert the AutoText.
- The Categories... button allows you to create new categories to classify your AutoTexts.
- Path... defines where to save the AutoTexts.
Editing an AutoText
In the AutoText dialog box (Edit → AutoText), you can edit your AutoText entries.
Select an existing AutoText, and choose the AutoText... button to modify or even eliminate the AutoText.
Selecting Edit, a document will open with the AutoText. Simply make the changes and save. The entry will now be available as edited.
| The changes will apply only to AutoTexts inserted after the modification, AutoText already inserted will not be changed |
Print a list of AutoText entries
- Choose Tools → Macros → Organize Macros → OpenOffice Basics.
- In the Macro from list, choose OpenOffice Macros → Gimmicks.
- Select AutoText and click Run .
- A list of the AutoText entries will be generated in a new document. You can print this document.