Difference between revisions of "Documentation/OOo3 User Guides/Calc Guide/Gallery of chart types"
(→Scatter or XY charts) |
(→Column and line charts) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
It is important to remember that while your data can be presented with a number of different charts, the message you want to convey to your audience dictates the chart you ultimately use. The following sections present examples of the types of charts that Calc provides, with some of the tweaks that each sort can have and some notes as to what purpose you might have for that chart type. For details, see the Help. | It is important to remember that while your data can be presented with a number of different charts, the message you want to convey to your audience dictates the chart you ultimately use. The following sections present examples of the types of charts that Calc provides, with some of the tweaks that each sort can have and some notes as to what purpose you might have for that chart type. For details, see the Help. | ||
| − | == | + | == Column charts == |
''Column charts'' are commonly used for data that shows trends over time. They are best for charts that have a relatively small number of data points. (For large time series a line chart would be better.) It is the default chart type, as it is one of the most useful charts and the easiest to understand. | ''Column charts'' are commonly used for data that shows trends over time. They are best for charts that have a relatively small number of data points. (For large time series a line chart would be better.) It is the default chart type, as it is one of the most useful charts and the easiest to understand. | ||
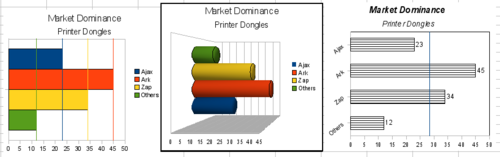
| − | == | + | == Bar charts == |
[[Image:CG3Ch4F24.png|thumb|none|500px|''Three bar graph treatments.'']] | [[Image:CG3Ch4F24.png|thumb|none|500px|''Three bar graph treatments.'']] | ||
| − | + | ''Bar charts'' are excellent for giving an immediate visual impact for data comparison where time is not important, for example to compare the popularity of a few products in a marketplace. | |
| − | * | + | * The first chart is achieved quite simply by using the chart wizard with '''Insert > Grids''', deselecting y-axis, and using '''Insert > Mean Value Lines'''. |
| − | * | + | * The second chart is the 3D option in the chart wizard with a simple border and the 3D chart area twisted around. |
| − | * | + | * The third chart is an attempt to get rid of the legend and put labels showing the names of the companies on the axis instead. We also changed the colors to a hatch pattern. |
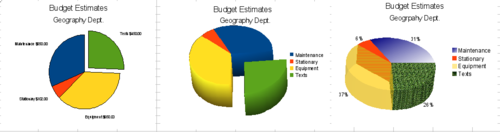
| − | == | + | == Pie charts == |
| − | + | ''Pie charts'' are excellent when you need to compare proportions. For example, comparisons of departmental spending: what the department spent on different items or what different departments spent. They work best with smaller numbers of values, about half a dozen; more than this and the visual impact begins to fade. | |
| − | + | As the Chart Wizard guesses the series that you wish to include in your pie chart, you might need to adjust this initially on the Wizard’s Data Ranges page if you know you want a pie chart, or by using the '''Format > Data Ranges > Data Series''' dialog. | |
| − | + | You can do some interesting things with a pie chart, especially if you make it into a 3D chart. It can then be tilted, given shadows, and generally turned into a work of art. Just don’t clutter it so much that your message is lost, and be careful that tilting does not distort the relative size of the segments. | |
| − | + | You can choose in the Chart Wizard to explode the pie chart, but this is an all or nothing option. If your aim is to accentuate one piece of the pie, you can separate out one piece by carefully highlighting it after you have finished with the Chart Wizard, and dragging it out of the pie plate. When you do this you might need to enlarge the chart area again to regain the original size of the pieces. | |
| + | |||
| + | You can choose in the Chart Wizard to explode the pie chart, but this is an all or nothing option. If your aim is to accentuate one piece of the pie, you can separate out one piece by carefully highlighting it after you have finished with the Chart Wizard, and dragging it out of the group. When you do this you might need to enlarge the chart area again to regain the original size of the pieces. | ||
[[Image:CG3Ch4F25.png|thumb|none|500px|''Pie charts'']] | [[Image:CG3Ch4F25.png|thumb|none|500px|''Pie charts'']] | ||
| − | + | The effects achieved in the figure above are explained below. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | * 2D pie chart with one part of the pie exploded. Choose '''Insert > Legend''' and deselect the ''Display legend'' box. Choose '''Insert > Data Labels''' and choose ''Show value as number''. Then carefully select the piece you wish to highlight, move the cursor to the edge of the piece and click (the piece will have nine green highlight squares to mark it), and then drag it out from the rest of the pieces. The pieces will decrease in size, so you need to highlight the chart wall and drag it at a corner to increase the size. | |
| + | * 3D pie chart with realistic schema and illumination. Choose '''Format > 3D view > Illumination''' where you can change the direction of the light, the color of the ambient light, and the depth of the shade. We also adjusted the 3D angle of the disc in the ''Perspective ''dialog on the same set of tabs.<br/>The chart updates as you make changes, so you can immediately see the effects.<br/>If you want to separate out one of the pieces, click on it carefully; you should see a wire frame highlight. Drag it out with the mouse and like the 2D chart you need to increase the size of the chart wall. | ||
| + | * 3D pie chart with different fill effects in each portion of the pie. Choose '''Insert > Data labels''' and select ''Show value as percentage''. Then carefully select each of the pieces so that it has a wire frame highlight and right-click to get the object properties dialog; choose the ''Area'' tab. For one we chose a bitmap, for another a gradient and for the third we used the ''Transparency'' tab and adjusted the transparency to 50%. | ||
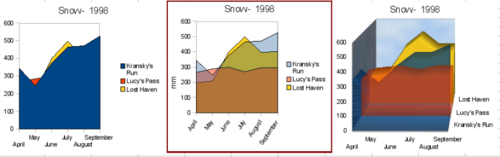
| − | == | + | == Area charts == |
An ''area chart'' is a version of a line or column graph. It may be useful where you wish to emphasize volume of change. Area charts have a greater visual impact than a line chart, but the data you use will make a difference. | An ''area chart'' is a version of a line or column graph. It may be useful where you wish to emphasize volume of change. Area charts have a greater visual impact than a line chart, but the data you use will make a difference. | ||
[[Image:CG3Ch4F27.png|thumb|none|500px|''Area charts—the good, the bad, and the ugly'']] | [[Image:CG3Ch4F27.png|thumb|none|500px|''Area charts—the good, the bad, and the ugly'']] | ||
| − | As shown above, an area chart is sometimes tricky to use. This may be one good reason to use transparency values in an area chart. | + | As shown above, an area chart is sometimes tricky to use. This may be one good reason to use transparency values in an area chart. After setting up the basic chart using the Chart Wizard, do this: |
| + | * Right-click on the Y axis and choose '''Delete Major Grid'''. As the data overlaps, some of it is missing behind the first data series. This is not what you want. A better solution is shown in Chart 2. | ||
| + | * After deselecting the Y axis grid, right-click on each data series in turn and choose '''Format Data Series'''. On the Transparency tab, set ''Transparency'' to 50%. The transparency makes it easy to see the data hidden behind the first data series. Now, right-click on the X axis and choose '''Format Axis'''. On the Label tab, choose '''Tile''' in the ''Order'' section and set the ''Text orientation'' to 55 degrees. This places the long labels at an angle. | ||
| + | * To create the third variation, after doing the steps above, right-click and choose '''Chart Type'''. Choose the '''3D Look''' option and select '''Realistic''' from the drop-down list. We also twisted the chart area around and gave the chart wall a picture of the sky. As you can see, the legend turns into labels on the z-axis. But overall, though it is visually more appealing, it is more difficult to see the point you are trying to make with the data. | ||
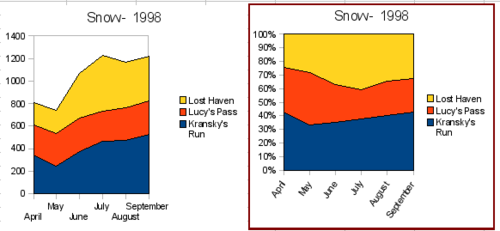
| − | + | Other ways of visualizing the same data series are represented by the stacked area chart or the percentage stacked area chart. The first does what it says: each number of each series is added to the others so that it shows an overall volume but not a comparison of the data. The percentage stacked chart shows each value in the series as a part of the whole. For example in June all three values are added together and that number represents 100%. The individual values are a percentage of that. Many charts have varieties which have this option. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | Other ways of visualizing the same data series are represented by the stacked area chart or the percentage stacked area chart. The first does what it says | + | |
[[Image:CG3Ch4F28.png|thumb|none|500px|''Stacked and percentage stacked area charts'']] | [[Image:CG3Ch4F28.png|thumb|none|500px|''Stacked and percentage stacked area charts'']] | ||
| − | == | + | == Line charts == |
| − | + | A ''line chart'' is a time series with a progression. It is ideal for raw data, and useful for charts with plentiful data that shows trends or changes over time where you want to emphasize continuity. On line charts, the x-axis is ideal to represent time series data. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | Things to do with lines: thicken them | + | Things to do with lines: thicken them, make them 3D, smooth the contours, just use points. |
3D lines confuse the viewer, so just using a thicker line often works better. | 3D lines confuse the viewer, so just using a thicker line often works better. | ||
| Line 74: | Line 61: | ||
[[Image:CG3Ch4F29.png|thumb|none|500px|''Line charts'']] | [[Image:CG3Ch4F29.png|thumb|none|500px|''Line charts'']] | ||
| − | == | + | == Scatter or XY charts == |
| − | ''Scatter charts'' are great for visualizing data that you have not had time to analyze, and they may be the best for data when you have a constant value with which to compare the data; for example, weather data, reactions under different acidity levels, conditions at altitude, or any data which matches two series of numeric data. In contrast to line charts, the x-axis are the left to right labels which usually indicate a time series. | + | ''Scatter charts'' are great for visualizing data that you have not had time to analyze, and they may be the best for data when you have a constant value with which to compare the data; for example, weather data, reactions under different acidity levels, conditions at altitude, or any data which matches two series of numeric data. In contrast to line charts, the x-axis are the left to right labels, which usually indicate a time series. |
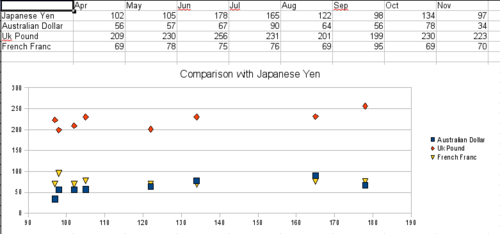
[[Image:CG3Ch4F30.png|thumb|none|500px|''A particularly volatile time in the world currency market.'']] | [[Image:CG3Ch4F30.png|thumb|none|500px|''A particularly volatile time in the world currency market.'']] | ||
| − | + | Scatter charts may surprise those unfamiliar with how they work. While constructing the chart, if you choose '''Data Range > Data series in rows''', the first row of data represents the x-axis. The rest of the rows of data are then compared against the first row data. The figure above shows a comparison of three currencies with the Japanese Yen. Even though the table presents the monthly series, the chart does not. In fact the Japanese Yen does not appear; it is merely used as the constant series that all the other data series are compared against. | |
| + | |||
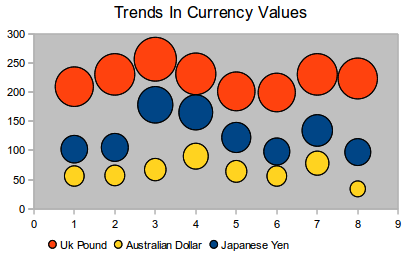
| + | ==Bubble charts== | ||
| + | A bubble chart is a variation of a scatter chart in which the data points are replaced with bubbles. It shows the relations of three variables in two dimensions. Two variables are used for the position on the X-axis and Y-axis, while the third is shown as the relative size of each bubble. One or more data series can be included in a single chart. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bubble charts are often used to present financial data. The data series dialog for a bubble chart has an entry to define the data range for the bubbles and their sizes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:CG3Ch4F30a.png|thumb|none|500px|''Bubble chart showing three data series.'']] | ||
== Net charts == | == Net charts == | ||
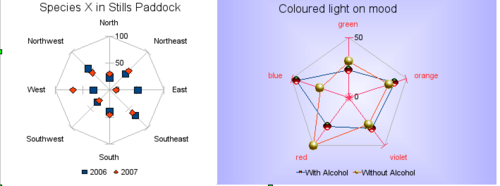
| − | A ''net chart'' is similar to polar or radar | + | A ''net chart'' is similar to polar or radar chart. They are useful for comparing data that are not time series, but show different circumstances, such as variables in a scientific experiment or direction. The poles of the net chart are equivalent to the y-axes of other charts. Generally, between three and eight axes are best; any more and this type of chart becomes confusing. Before and after values can be plotted on the same chart, or perhaps expected and real results, so that differences can be compared. |
[[Image:CG3Ch4F31.png|thumb|none|500px|''Two net diagrams showing totally fabricated data from totally fictional experiments.'']] | [[Image:CG3Ch4F31.png|thumb|none|500px|''Two net diagrams showing totally fabricated data from totally fictional experiments.'']] | ||
| − | + | The figure above shows two types of net charts: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | There are also varieties of net chart that show the data series as stacked numbers or stacked percentages. | + | * (Left): Plain net chart without grids and with just points, no lines. |
| + | * (Right): Net chart with lines, points and grid. Axes colors and labels changed. Chart area color = gradient. Points changed to fancy 3D ones. | ||
| + | |||
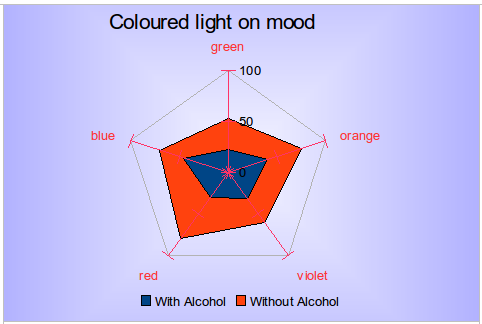
| + | There are also varieties of net chart that show the data series as stacked numbers or stacked percentages. The series can also be filled with a color (Figure 29). Partial transparency is often best for showing all the series. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:CG3Ch4F31a.png|thumb|none|500px|''Filled net or radar chart.'']] | ||
== Stock charts == | == Stock charts == | ||
| Line 107: | Line 105: | ||
[[Image:CG3Ch4F33.png|thumb|none|500px|''Column and line chart'']] | [[Image:CG3Ch4F33.png|thumb|none|500px|''Column and line chart'']] | ||
| − | + | This chart has manufacturing costs and profit data for two products over a period of time (six months in 2007). To creat this chart, highlighted the table and start the Chart Wizard. Choose the Column and Line chart type with two lines and the data series in rows. Then give it a title to highlight the aspect you want to show. The lines are different colors at this stage and don’t reflect the product relationships. When you finish with the Chart Wizard, highlight the chart, click on the line, right-click, and choose '''Format Data Series'''. | |
| + | |||
| + | On this tab there are a few things to change. The colors should match the products, so both Ark Manufacturing and profit are blue and Prall is red. The lines need to be more noticeable so make the lines thicker by increasing the width to 0.08. | ||
| − | + | For the background, highlight the chart wall, right-click and choose '''Format Wall'''. On the ''Area'' tab, change the drop-down box to show Gradient. Choose one of the preset gradient patterns and make it lighter by going to the ''Transparency'' tab and making the gradient 50% transparent. | |
| − | + | To make the chart look cleaner without the grid, go to '''Insert > Grids''' and deselect the X-axis option. | |
| − | |||
{{CCBY}} | {{CCBY}} | ||
[[Category: Calc Guide (Documentation)]] | [[Category: Calc Guide (Documentation)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:19, 9 December 2010
It is important to remember that while your data can be presented with a number of different charts, the message you want to convey to your audience dictates the chart you ultimately use. The following sections present examples of the types of charts that Calc provides, with some of the tweaks that each sort can have and some notes as to what purpose you might have for that chart type. For details, see the Help.
Contents
Column charts
Column charts are commonly used for data that shows trends over time. They are best for charts that have a relatively small number of data points. (For large time series a line chart would be better.) It is the default chart type, as it is one of the most useful charts and the easiest to understand.
Bar charts
Bar charts are excellent for giving an immediate visual impact for data comparison where time is not important, for example to compare the popularity of a few products in a marketplace.
- The first chart is achieved quite simply by using the chart wizard with Insert > Grids, deselecting y-axis, and using Insert > Mean Value Lines.
- The second chart is the 3D option in the chart wizard with a simple border and the 3D chart area twisted around.
- The third chart is an attempt to get rid of the legend and put labels showing the names of the companies on the axis instead. We also changed the colors to a hatch pattern.
Pie charts
Pie charts are excellent when you need to compare proportions. For example, comparisons of departmental spending: what the department spent on different items or what different departments spent. They work best with smaller numbers of values, about half a dozen; more than this and the visual impact begins to fade.
As the Chart Wizard guesses the series that you wish to include in your pie chart, you might need to adjust this initially on the Wizard’s Data Ranges page if you know you want a pie chart, or by using the Format > Data Ranges > Data Series dialog.
You can do some interesting things with a pie chart, especially if you make it into a 3D chart. It can then be tilted, given shadows, and generally turned into a work of art. Just don’t clutter it so much that your message is lost, and be careful that tilting does not distort the relative size of the segments.
You can choose in the Chart Wizard to explode the pie chart, but this is an all or nothing option. If your aim is to accentuate one piece of the pie, you can separate out one piece by carefully highlighting it after you have finished with the Chart Wizard, and dragging it out of the pie plate. When you do this you might need to enlarge the chart area again to regain the original size of the pieces.
You can choose in the Chart Wizard to explode the pie chart, but this is an all or nothing option. If your aim is to accentuate one piece of the pie, you can separate out one piece by carefully highlighting it after you have finished with the Chart Wizard, and dragging it out of the group. When you do this you might need to enlarge the chart area again to regain the original size of the pieces.
The effects achieved in the figure above are explained below.
- 2D pie chart with one part of the pie exploded. Choose Insert > Legend and deselect the Display legend box. Choose Insert > Data Labels and choose Show value as number. Then carefully select the piece you wish to highlight, move the cursor to the edge of the piece and click (the piece will have nine green highlight squares to mark it), and then drag it out from the rest of the pieces. The pieces will decrease in size, so you need to highlight the chart wall and drag it at a corner to increase the size.
- 3D pie chart with realistic schema and illumination. Choose Format > 3D view > Illumination where you can change the direction of the light, the color of the ambient light, and the depth of the shade. We also adjusted the 3D angle of the disc in the Perspective dialog on the same set of tabs.
The chart updates as you make changes, so you can immediately see the effects.
If you want to separate out one of the pieces, click on it carefully; you should see a wire frame highlight. Drag it out with the mouse and like the 2D chart you need to increase the size of the chart wall. - 3D pie chart with different fill effects in each portion of the pie. Choose Insert > Data labels and select Show value as percentage. Then carefully select each of the pieces so that it has a wire frame highlight and right-click to get the object properties dialog; choose the Area tab. For one we chose a bitmap, for another a gradient and for the third we used the Transparency tab and adjusted the transparency to 50%.
Area charts
An area chart is a version of a line or column graph. It may be useful where you wish to emphasize volume of change. Area charts have a greater visual impact than a line chart, but the data you use will make a difference.
As shown above, an area chart is sometimes tricky to use. This may be one good reason to use transparency values in an area chart. After setting up the basic chart using the Chart Wizard, do this:
- Right-click on the Y axis and choose Delete Major Grid. As the data overlaps, some of it is missing behind the first data series. This is not what you want. A better solution is shown in Chart 2.
- After deselecting the Y axis grid, right-click on each data series in turn and choose Format Data Series. On the Transparency tab, set Transparency to 50%. The transparency makes it easy to see the data hidden behind the first data series. Now, right-click on the X axis and choose Format Axis. On the Label tab, choose Tile in the Order section and set the Text orientation to 55 degrees. This places the long labels at an angle.
- To create the third variation, after doing the steps above, right-click and choose Chart Type. Choose the 3D Look option and select Realistic from the drop-down list. We also twisted the chart area around and gave the chart wall a picture of the sky. As you can see, the legend turns into labels on the z-axis. But overall, though it is visually more appealing, it is more difficult to see the point you are trying to make with the data.
Other ways of visualizing the same data series are represented by the stacked area chart or the percentage stacked area chart. The first does what it says: each number of each series is added to the others so that it shows an overall volume but not a comparison of the data. The percentage stacked chart shows each value in the series as a part of the whole. For example in June all three values are added together and that number represents 100%. The individual values are a percentage of that. Many charts have varieties which have this option.
Line charts
A line chart is a time series with a progression. It is ideal for raw data, and useful for charts with plentiful data that shows trends or changes over time where you want to emphasize continuity. On line charts, the x-axis is ideal to represent time series data.
Things to do with lines: thicken them, make them 3D, smooth the contours, just use points.
3D lines confuse the viewer, so just using a thicker line often works better.
Scatter or XY charts
Scatter charts are great for visualizing data that you have not had time to analyze, and they may be the best for data when you have a constant value with which to compare the data; for example, weather data, reactions under different acidity levels, conditions at altitude, or any data which matches two series of numeric data. In contrast to line charts, the x-axis are the left to right labels, which usually indicate a time series.
Scatter charts may surprise those unfamiliar with how they work. While constructing the chart, if you choose Data Range > Data series in rows, the first row of data represents the x-axis. The rest of the rows of data are then compared against the first row data. The figure above shows a comparison of three currencies with the Japanese Yen. Even though the table presents the monthly series, the chart does not. In fact the Japanese Yen does not appear; it is merely used as the constant series that all the other data series are compared against.
Bubble charts
A bubble chart is a variation of a scatter chart in which the data points are replaced with bubbles. It shows the relations of three variables in two dimensions. Two variables are used for the position on the X-axis and Y-axis, while the third is shown as the relative size of each bubble. One or more data series can be included in a single chart.
Bubble charts are often used to present financial data. The data series dialog for a bubble chart has an entry to define the data range for the bubbles and their sizes.
Net charts
A net chart is similar to polar or radar chart. They are useful for comparing data that are not time series, but show different circumstances, such as variables in a scientific experiment or direction. The poles of the net chart are equivalent to the y-axes of other charts. Generally, between three and eight axes are best; any more and this type of chart becomes confusing. Before and after values can be plotted on the same chart, or perhaps expected and real results, so that differences can be compared.
The figure above shows two types of net charts:
- (Left): Plain net chart without grids and with just points, no lines.
- (Right): Net chart with lines, points and grid. Axes colors and labels changed. Chart area color = gradient. Points changed to fancy 3D ones.
There are also varieties of net chart that show the data series as stacked numbers or stacked percentages. The series can also be filled with a color (Figure 29). Partial transparency is often best for showing all the series.
Stock charts
A stock chart is a specialized column graph specifically for stocks and shares. You can choose traditional lines, candlestick, and two-column type charts. The data required for these charts is quite specialized, with series for opening price, closing price, and high and low prices. Of course the x-axis represents a time series.
When you set up a stock chart in the Chart Wizard, the Data Series dialog is very important. You need to tell it which series is for the opening price, closing price, high and low price of the stock, or else the chart may be indecipherable. The sample table for this chapter needed to be changed to fit the data series.
A nice touch is that OpenOffice.org Chart color-codes the rising and falling shares: white for rising and black for falling in the candlestick chart, and red and blue in the traditional line chart.
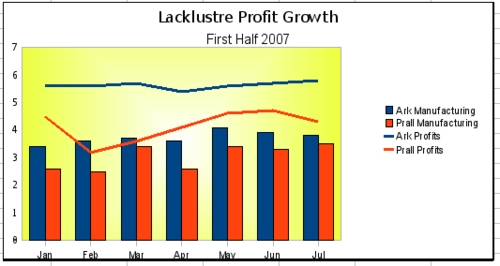
Column and line charts
A column and line chart is a combination of two other chart types. It is useful for combining two distinct but related data series, for example sales over time (column) and the profit margin trends (line).
You can choose the number of columns and lines in the Chart Wizard. So for example you might have two columns with two lines to represent two product lines with the sales figures and profit margins of both.
This chart has manufacturing costs and profit data for two products over a period of time (six months in 2007). To creat this chart, highlighted the table and start the Chart Wizard. Choose the Column and Line chart type with two lines and the data series in rows. Then give it a title to highlight the aspect you want to show. The lines are different colors at this stage and don’t reflect the product relationships. When you finish with the Chart Wizard, highlight the chart, click on the line, right-click, and choose Format Data Series.
On this tab there are a few things to change. The colors should match the products, so both Ark Manufacturing and profit are blue and Prall is red. The lines need to be more noticeable so make the lines thicker by increasing the width to 0.08.
For the background, highlight the chart wall, right-click and choose Format Wall. On the Area tab, change the drop-down box to show Gradient. Choose one of the preset gradient patterns and make it lighter by going to the Transparency tab and making the gradient 50% transparent.
To make the chart look cleaner without the grid, go to Insert > Grids and deselect the X-axis option.
| Content on this page is licensed under the Creative Common Attribution 3.0 license (CC-BY). |